A good Product Manager has the skills to inspire their team and convince executives why they should build this vs. that. Being an expert in customer development, a product manager is responsible for knowing what to build, why and when. In many ways a product manager's role is what holds an entire organization together, no matter how big or small the company may be.

From leading a team, developing valuable products and launching on time and within budget, to making sure the company profits from products that effectively serve a target audience -- a product manager has to have their eyes in every department.
Judging by the high demand for product managers in every new growing business, it is easy to say that more and more young professionals nowadays are showing a growing interest in this career-line. But do you know what it takes to become a good product manager? Are you clear on the skills a product manager needs to get the job done?
In this article, we share important pointers you can follow when walking down the path of becoming the next best product manager in just about any industry.

A product manager needs to have many different skills that will set him/her apart from the rest in a sea of potential candidates. However, did you know that each skill is also prioritized and categorized in a hierarchy?
This seniority hierarchy is what allows the employer to know which skill is present in abundance in the employee, where the candidate needs skills work, and if he/she will even be a good fit for the organization on a long-term basis.
The Most Important Skills for Product Managers
Every product manager is different, and you should find your own style based on what works best for you. But there are a well agreed list of the most important skills every product manager should possess to kill it in any organization.
Interpersonal Skills
Product managers must have amazing interpersonal skills if they want to get everyone on board. When you are part of team working on a new product or service, product managers must take a leadership role. And a good leader is be someone who can get along with everyone involved, while still finding a way to empower team members and make an individual contribution to the project.
Product managers must do this at scale -- interacting with various teams within an organization. From making sure the team members know what should be done, to handling customers and stakeholders, a good product manager will use his or her interpersonal skills to get everyone working at their best, while also balancing out the technical aspects related to the project.

In other words, interpersonal skills here mean being able to actively listen to what each member of the team is trying to say while also negotiating and coming to solid conclusions that will mean a win-win for both or more parties.
Seeing the Big Picture
If you want to be a great product manager, know that a crucial skill to master is becoming a jack of all trades. Unlike department managers, sales managers, and/or general managers, a product manager’s role is much more diverse and not necessarily limited to one area of the business.
In a way, the product manager is the person everyone will go to when it comes to determining which product or concept is to be launched, probable challenges the product may face, and how an issue can be resolved.
A good PM needs to understand the bigger picture, the impact to all stakeholders, and address the challenges found in the organization.
But that doesn’t mean a PM will simply ignore the small stuff. If you want to take up the career of a product manager in a growing industry, you have to start treating every problem like a big one. A product manager can get to the root of an issue only when he/she treats it as a fatal one; for the whole organization and not just the product itself.
Strategic Thinking
First and foremost, strategic thinking is one of the most important skills a product manager can have. With proper and efficient strategic thinking skills, a good PM can easily answer and come to smart conclusions on tricky questions without wasting valuable time or losing productivity.

Strategic thinking also allows the product manager to brainstorm with the team using an internal knowledge base and become an expert on the question at hand. Of course, this kind of skill does not develop overnight. The best PM’s hone those skills with time.
Communication and Writing
Proper communication is a key aspect for many product managers, regardless of their seniority or priority in the workplace.
A good product manager should have stellar communicative skills that can easily captivate a large audience. Clear communication skills also include the ability to write and create proper and informative emails, drafts, product requirements documents and any other piece of information required to persuade a customer, stakeholder, or team member.
Certain tools that allow you easy virtual planning can assist in enhancing your communication skills. For example, product managers use tools like Markup Hero that support PDF and image annotation or Notion for creating requirements documents. You should develop a product manager toolbox with software that can help you explain your ideas and organize your thoughts.

Collaboration and Empowerment
If you want to achieve success as a product manager, you will need to learn how to stay active throughout the day (possibly during the night, too, in some cases!). From participating and organizing large meetings to solving physical problems on-field, a lot of sectors demand the overview of a product manager.
The key aspect to remember here is become a master of conflict resolution, even if it means alternating between choices and initial objectives.
Technical Talent
From writing captivating and informative case studies to keeping oneself updated with the latest trends on the market, product management work goes deep and beyond the simple objectives and missions of an organization.

As a product manager, one has to perform analytics on various trends and future forecasts, therefore creating a substantial report for every department of the organization. The PM should define next steps for various stakeholders and identify risks that might negatively affect product success or company profits.
A product manager can never be successful if he/she doesn’t learn how to balance between soft and technical skills. While showing empathy and being communicative and open in the workplace, a product manager also needs to have in-depth knowledge regarding the technical aspect of being a PM.
This includes being able to excel in data science, various analytics, legal issues, and jargon, including safety measures and regulations. And of course, the PM should have a clear understanding of Search Engine Optimization (SEO) and how it can contribute to a product’s launch.
Qualitative and Detail Oriented
Similar to an entrepreneur, a product manager also has to keep keen eye on problem identification, always on the lookout for new opportunities to meet the needs of customers.
In this case, a product manager will complete multiple checks on every product that reaches him while also spending a substantial period with its users. According to ProductPlan, thorough qualitative research allows product managers to see and spot trends in surveys, which can, therefore, assist in future product launches and concept planning.
Empathy and Motivation
The product manager needs to have a way with his/her words that will allow him/her to persuade and convince the target audience. It is the job of a product manager to have an idea about everything there is to know regarding a product.
The work of a product manager is to captivate the audience, the customer, stakeholder, and everyone in between. This might be done through principled negotiation where the product manager will have specific goals to achieve through a meeting while maintaining a healthy relationship with the team members, or simply listen to what your team has to say.

Product managers, who are often seen as the CEO of a product line, are those who shows passion and empathy towards customers. However, showing empathy is not constricted towards customers only, as your subordinates and teammates deserve the same behavior and attitude from you.
You can generate trust and a feeling of safety in the workplace by investing your time in developing psychological safety. All that is required here is for the product manager to simply make tweaks to some words to create openness in the work-area that will assist workers in voicing out their opinions.
Software and Sciences
Use popular tools like Pendo or SurveyMonkey to assist with product management functions. Such tools are beneficial for product managers as they allow PMs to check surveys, inquiries, product analytics, hands-off observations, etc.
Product managers can use these resources to analyze the intent of the users targeted for a potential product and their behavior towards it.
Team Management
A good product manager understands the key differences between product management and project management and know when the skills associated with each. Time management also plays a great role in the life and career of a product manager.
A product manager of a growing company will need to learn how to manage teams of engineers, product associates, project managers and even content marketing specialists.
Senior product managers will require even more responsibility and must hire and train junior PM’s or product management interns, guiding them towards success in the organization. On the other hand, every product manager will have to resort to technical communication and resources when collaborating with customers and stakeholders.
The management skills of a product manager can be the make or break for his/her career, as well as for the organization the product manager is working in.
5 Technical Skills Every Product Manager Must Have
Unlike soft skills, which can even assist you in your personal life, hard skills (technical skills) will have a direct impact on your work. For example, if you are in the health and beauty sector, a good hard skill will be to have an in-depth idea of the safety measures and legal issues associated with ingredients used in specific products.

Prioritization
You might not be aware of this, but having great prioritization skills is counted as a technical skill for a PM. Knowing how and when to say no directly to customers, investors, stakeholders, and generally, anyone directly associated with the business is a very important skill many PMs lack.
New product managers or those interested in this career can take a look at the Pareto Principle when it comes to developing and honing your prioritization skills.
R&D Proficiency
You cannot possibly be a successful product manager in any sector of your choice if you have no idea about the research and development that goes behind it. Not being able to analyze data, market research, and forecasts will mean the downfall of your career.
A good product manager will be able to decipher each data and also interpret it in the way most beneficial to the organization. The PM also needs to have a clear understanding of SEO and SQL to be able to maximize profit and success in the business and for the products.
Marketing
Product managers cannot excel in the industry without proper marketing skills. The entire concept of a product manager revolves around researching, developing, promoting, and launching a product to the general audience. Good marketing skills will allow the PM to become flexible with each new trend while also developing newer and better strategies for different products.
UX, UI and Design
While UX product designing is generally assigned to a specific and separate individual, product managers with experience in this field are usually seen as superior and are given more priority.
Even the most basic knowledge in UX design can assist a product manager and a typical UX designer in creating the best team in the industry.
Strategic Thinking
Product managers need to have a deep understanding of each phase in the development of a product. Project management will remain incomplete if the PM does not incorporate strategic thinking into the mix.
Strategic thinking allows a PM to know all about the lifecycle of the product being developed while also forecasting sales and market trends.
Career Path of a Product Manager
The career of a product manager is accomplished in several steps. A candidate cannot achieve the second or third role of a PM unless the basic primary role is taken up first-
- Associate Product Manager
- Product Manager
- Senior Product Manager
- Director of Product
- Vice President of Product
- Chief Product Officer, and so on.
Each of these roles requires the candidate to display a specific set of traits and characteristics. In a nutshell, the roles of the candidate usually go from showing basic interpersonal skills to demonstrating on-field knowledge and even managing an entire business itself.
Presenting Your Skills during a Job Search
When it comes to presenting your skills on a resume for a career as a PM, it is crucial to properly highlight your achievements and strengths concisely. You can present your achievements in a bullet-point format, where you can list down several ways your PM skills personally helped a business grow.
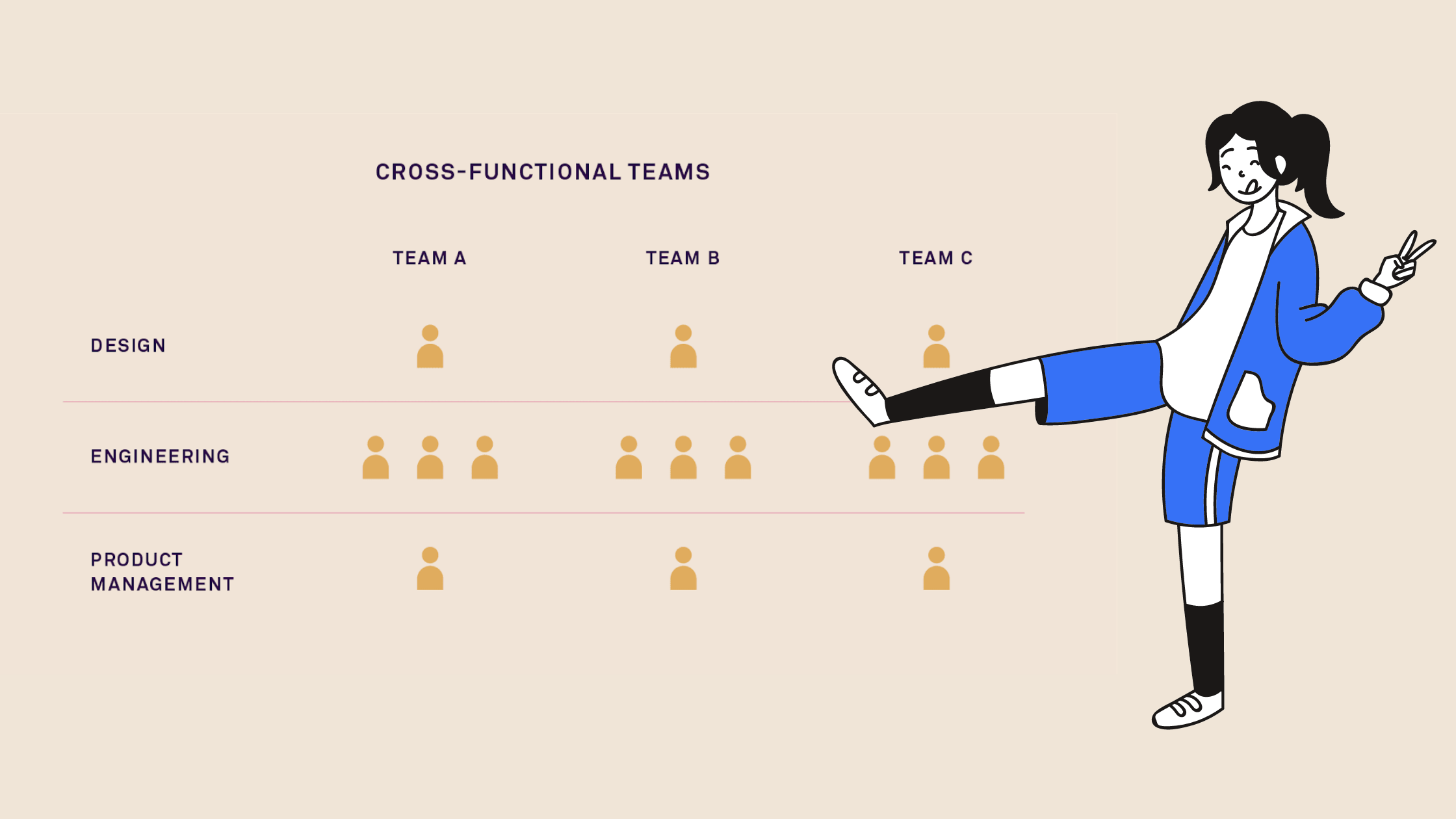
Cross-functional Skills for Product Managers
For those wanting to land a career as a cross-functional product manager or intern, some skills the candidate needs to have are:
- Good chemistry and relationship with the team
- Understand each member might have different opinions regarding an issue
- See the bigger picture and know how each skill of every member of the team might contribute to the project
- Communicate with the team and get your opinions across while also actively listening to their opinions.
Combine Hard and Soft Skills to Plummet Towards Success
By now, you probably have a clear understanding that a product manager can’t possibly become successful if he/she lacks either of the mentioned skills.
To achieve greatness in this growing industry, a PM needs to successfully combine both soft skills (i.e., empathy, communication, persuasion, creativity, etc.) and hard skills (i.e., data analysis, market research skills, strategic thinking, marketing, product development, etc.).
What People Ask about Product Managers
Here are some popular questions people ask about product managers you can use to see what gaps you might have in your skill set.
- What skills does a product manager need?
A PM needs to have interpersonal and hard skills that cater to customers and the stakeholder of a business. The skills vary from being able to be communicative to even do thorough data research daily. - What does a product manager do?
A product manager is responsible for overviewing the development and launch of a product while also assisting and guiding a cross-functional team towards improvement. - Do you think a college degree or any graduate degrees are important for landing a product manager role?
Yes, a Bachelor’s degree will allow you to land a primary level product manager role, while a Master’s degree will allow you to sit as a candidate for a senior or even higher level product manager role. - What are the core responsibilities in a current product manager role?
The core responsibilities are to lead a team while overseeing the entire project with the help of data analysis, proper communicative skills, and strategic thinking, etc. among many others. - What are the basic product management skills for SaaS?
Some product management skills for SaaS are knowing market trends, user behavior, soft and hard skills such as interpersonal skills and data analysis, efficient decision-making skills, etc. - Is Product Management a good career?
Yes, it is an extremely good career choice, especially if you’re living in the States. Product management holds the 4th position on Glassdoor’s 2019 list of best jobs in the states and salaries for product managers can go as high as 300K plus bonus and benefits.
Conclusion
A product manager’s skills are widely varied and are responsible for the make or break of an organization. Like most important roles, it takes time to become proficient. But climbing the product management career ladder is both satisfying and impactful.
With the right motivation, tools, tech, and potentially courses and training, a product manager can hone his/her skills while also learning more about the latest trends in the market.


